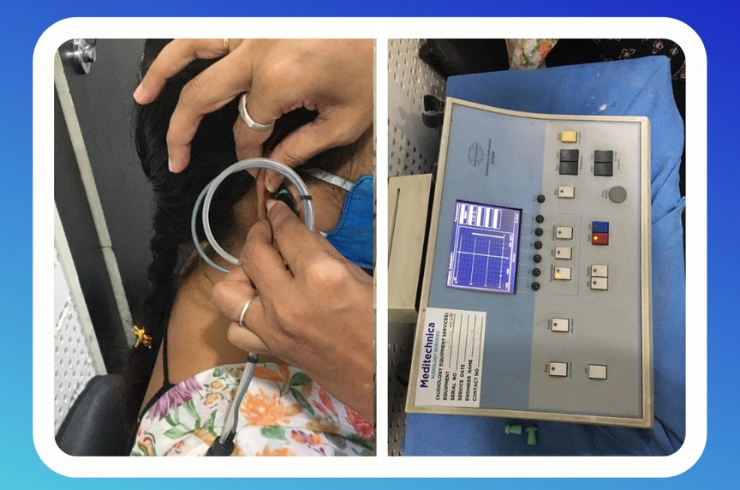
Immittance Audiometry is a test used to assess the middle ear’s function and the mobility of the eardrum. It helps in evaluating how well sound is transmitted through the ear canal to the inner ear. This test is primarily used to diagnose conditions affecting the middle ear, such as fluid in the ear, ear infections, or Eustachian tube dysfunction.
Tympanometry:
Acoustic Reflex Testing:
Static Compliance:
Immittance audiometry is useful for diagnosing:
Immittance audiometry provides valuable information for diagnosing non-sensorineural causes of hearing loss and is commonly used alongside pure-tone audiometry and speech audiometry to assess hearing health comprehensively.
Schedule your consultation today and start your journey to better health!